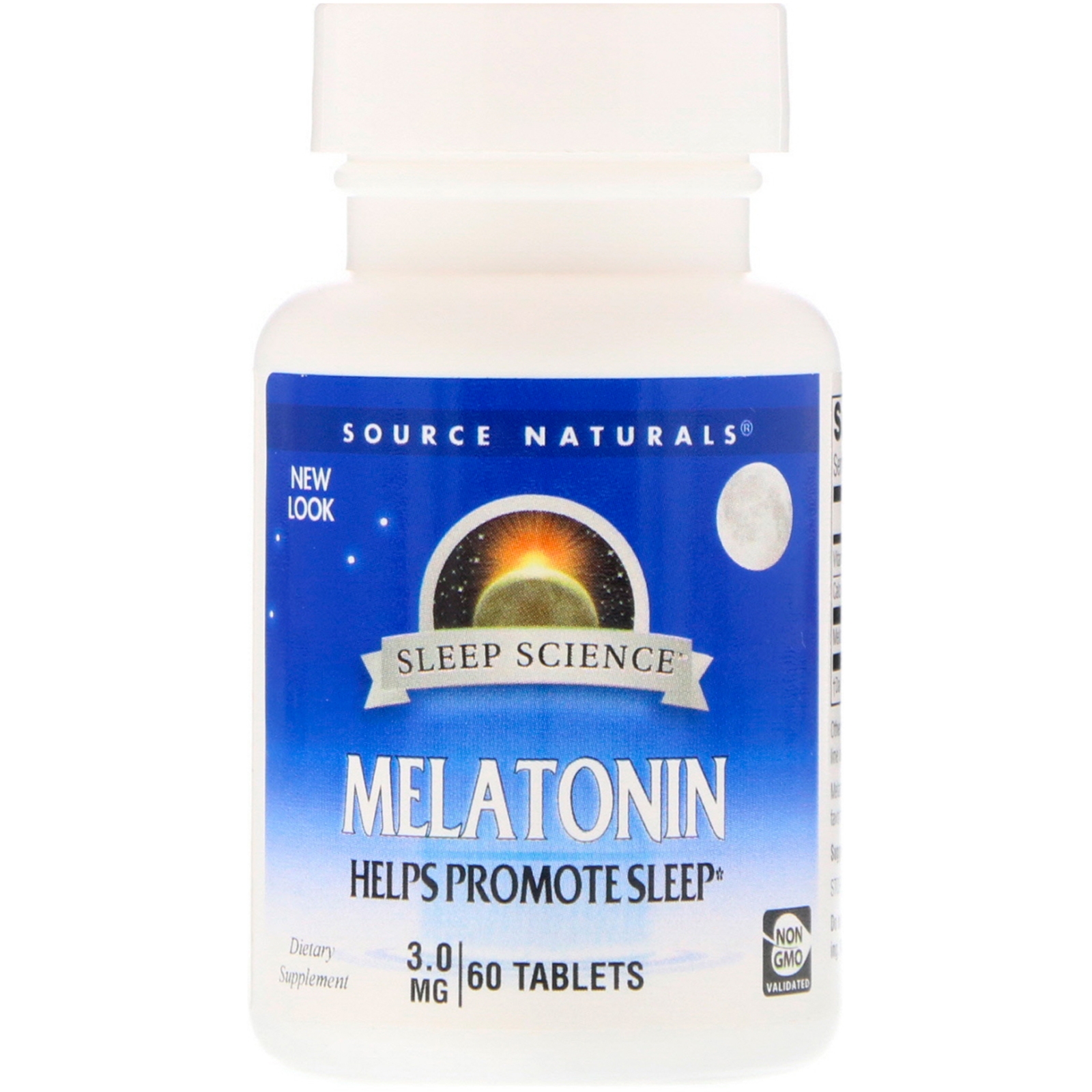
ส่งฟรีลงทะเบียนมีพร้อมส่งค่ะ Source Naturals Melatonin 3 mg 60 Tablets


| รหัสสินค้า | SourceNatural15 |
| หมวดหมู่ | Source Naturals |
| ราคาปกติ | |
| ลดเหลือ | 400.00 บาท |
| สถานะสินค้า | พร้อมส่ง |
| ลงสินค้า | 19 ก.ค. 2564 |
| อัพเดทล่าสุด | 19 ก.ค. 2564 |
| คงเหลือ | ไม่จำกัด |
| จำนวน | ชิ้น |
หยิบลงตะกร้า
รายละเอียดสินค้า
Source Naturals Melatonin is useful for occasional sleeplessness. Melatonin is a neurohormone produced in humans by the pineal gland. A favorite of travelers, it governs the body's circadian rhythms, helping the body ease into restful sleep. Melatonin is also a potent antioxidant. Source Naturals Timed Release Melatonin is formulated to allow for a gradual release of the active ingredient during an approximate six hour period. This provides the body with a more even absorption of melatonin. Melatonin is a natural hormone that regulates the human biological clock.
Where is Melatonin found? Melatonin is produced by the pineal gland, located within the brain. Levels of melatonin in the body fluctuate with the cycles of night and day. The highest melatonin levels are found at night. Melatonin is present in foods only in trace amounts.
Source Naturals Melatonin addresses the following body systems
Antioxidant Defense Free radicals are unstable, destructive molecules with one missing, unpaired electron. In a process called oxidation, the same process that turns iron to rust, free radicals can impact cells as they steal electrons from healthy molecules, starting a cascade that ages the body and affects the body cell by cell, tissue by tissue. This process is halted with antioxidants. Antioxidants selflessly donate their electrons to stabilize free radicals and prevent their effects. Free radicals are natural by-products of mitochondrial energy generation and they are also the result of constant bombardment by pollutants, toxins, excess sunlight, unnatural foods, and electromagnetic radiation. In 1954, Dr. Denham Haimen first espoused the Free Radical Theory of Aging. As we age, our body’s ability to produce innate antioxidants decreases, giving free radicals and the aging they cause the upper hand in our bodies. Supplementation with natural antioxidants can neutralize these harmful compounds.
Metabolism/Hormones At any moment, millions of biochemical reactions are taking place in or around our nearly 100 trillion cells. To function at high levels of health, our metabolism is constantly binding molecules together and breaking them apart. In a way, our health is a function of the ease, speed, and coordination of these myriad reactions, processes named methylation, acetylation, phosphorylation, and sulfation. Hormones are messengers that tell the body to begin its various physiological activities, such as growth or sexual development. Hormones are produced in our glands and are often triggered by the brain. They are part of the intricate mechanism that makes us humans with unique personalities.
Through phospholipids such as omega-3 or omega-6 in the membrane of the cell, the hormones transfer important messages to the nucleus of the cell where the DNA produces the proteins and enzymes needed to carry out the brain's desires. With age, as metabolism slows, can come a loss of effective function, which in turn can lead to a multitude of problems associated with aging. By proactively supporting metabolic and hormonal processes you can maintain youthful activity within your body.
Cognition / Nerves The human brain is the most complex structure known to man; much of how it functions and enables us to think, feel, contemplate abstract concepts, plan our future, and control many bodily processes is yet to be discovered. The function of the brain and nervous system is based on the unique structure of nerve cells (also called neurons), which take in and send out messages in the form of electrical impulses running through the phospholipids and minerals of the cell membranes. Although it is only two percent of our body weight, the brain consumes 20 percent of our energy. Neurotransmitters, brain chemicals that pass messages from one neuron to another, must be produced in adequate quantities to support mood, intelligence, concentration, assertiveness and calmness. This creates a tremendous need for nutritional fuel and energy. Brain functioning can be significantly improved by the right quantity and quality of nutrients.
Immune During the Plague of the 14th century, one-third of the population of Europe died. The question is: why did the others live, even though they were also exposed to the Yersinia pestis bacteria? The answer may be the strength and responsiveness of their immune systems. The immune system is like an intelligent second brain with the unique ability to identify foreign compounds and to quickly produce the specific defenses needed to combat harmful invaders and protect us. The immune system uses a wide variety of cells and biochemicals located primarily in the blood stream and the gastrointestinal tract, such as T-cells, B-cells, macrophages, and Natural Killer cells. We can significantly strengthen and improve the functionality of the immune system through nutrition, supplements and lifestyle modifications.


วิธีการชำระเงิน
ชำระเงินผ่านธนาคาร
ชำระเงินออนไลน์
- ค่าธรรมเนียม 3.9% + 11 THB
- การชำระผ่าน PayPal คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องแจ้งชำระเงิน เนื่องจากระบบจะจัดการให้คุณทันที ที่คุณชำระเงินเสร็จสมบูรณ์
สินค้าที่ดูล่าสุด
ค้นหาสินค้า
หมวดหมู่สินค้า
ติดต่อร้านค้า
0897769089
loveskinshop@hotmail.com
สมาชิก
คุณเป็นตัวแทนจำหน่าย
- ระดับ{{userdata.dropship_level_name}}
- ไปหน้าหลักตัวแทน
ระดับสมาชิกของคุณ ที่ร้านค้านี้
รายการสั่งซื้อของฉัน
- ทั้งหมด {{(order_nums && order_nums.all)?'('+order_nums.all+')':''}}
- รอการชำระเงิน {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_payment)?'('+order_nums.wait_payment+')':''}}
- รอตรวจสอบยอดเงิน {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_payment_verify)?'('+order_nums.wait_payment_verify+')':''}}
- รอจัดส่งสินค้า {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_send)?'('+order_nums.wait_send+')':''}}
- รอยืนยันได้รับสินค้า {{(order_nums && (order_nums.wait_receive || order_nums.wait_confirm))?'('+(order_nums.wait_receive+order_nums.wait_confirm)+')':''}}
- รอตรวจสอบข้อร้องเรียน {{(order_nums && order_nums.dispute)?'('+order_nums.dispute+')':''}}
- เรียบร้อยแล้ว {{(order_nums && order_nums.completed)?'('+order_nums.completed+')':''}}
- ทั้งหมด {{(order_nums && order_nums.all)?'('+order_nums.all+')':''}}
- รอการชำระเงิน {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_payment)?'('+order_nums.wait_payment+')':''}}
- รอตรวจสอบยอดเงิน{{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_payment_verify)?'('+order_nums.wait_payment_verify+')':''}}
- รอจัดส่งสินค้า {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_send)?'('+order_nums.wait_send+')':''}}
- ส่งสินค้าเรียบร้อยแล้ว {{(order_nums && order_nums.sent)?'('+order_nums.sent+')':''}}
 loveskinshop
loveskinshop
{{is_joined?'เป็นสมาชิกแล้ว':'Join เป็นสมาชิกร้าน'}}
4
สมัครสมาชิกร้านนี้ เพื่อรับสิทธิพิเศษ
หน้าแรก | วิธีการสั่งซื้อสินค้า | แจ้งชำระเงิน | บทความ | เว็บบอร์ด | เกี่ยวกับเรา | ติดต่อเรา | ตะกร้าสินค้า | Site Map









ร้านค้าออนไลน์
Inspired by
LnwShop.com (v2)
คุณมีสินค้า 0 ชิ้นในตะกร้า สั่งซื้อทันที
สินค้าในตะกร้า ({{total_num}} รายการ)

ขออภัย ขณะนี้ยังไม่มีสินค้าในตะกร้า
ราคาสินค้าทั้งหมด
฿ {{price_format(total_price)}}
- ฿ {{price_format(discount.price)}}
ราคาสินค้าทั้งหมด
{{total_quantity}} ชิ้น
฿ {{price_format(after_product_price)}}
ราคาไม่รวมค่าจัดส่ง
➜ เลือกซื้อสินค้าเพิ่ม


